Latest • 36 videos
The Messenger explores our deep-seated connection to birds and warns that the uncertain fate of songbirds might mirror our own. Moving from the northern reaches of the Boreal Forest to the base of Mount Ararat in Turkey to the streets of New York, The Messenger brings us face-to-face with a remarkable variety of human-made perils that have devastated thrushes, warblers, orioles, tanagers, grosbeaks and many other airborne music-makers. In ancient times humans looked to the flight and songs of birds to protect the future. Today once again, birds have something to tell us.
2015 • Nature
Tells the story of the Sinclair ZX Spectrum. This film goes into all the finer details of how and why the ZX Spectrum was created, what impact the computer had as well as the various versions that followed right the way through to the latest iteration of the system with the ZX Spectrum Next. Complete with interviews from industry legends.
2024 • Technology
Luminous tells the story of the first astronomer in history to publicly predict the near-future explosion of a star--will he be right? Others in the astronomical community are skeptical, and professional reputations hang in the balance. In production for five years, Luminous follows Larry Molnar's journey to test an unprecedented prediction, knowing that its success or failure will unfold squarely in the international spotlight.
2022 • Astronomy
When Apollo astronaut Gene Cernan stepped on the Moon in December 1972 he left his footprints and his daughter's initials in the lunar dust. Only now, over forty years later, is he ready to share his epic but deeply personal story of fulfillment, love and loss. Cernan's burning ambition carried him from a quiet Chicago suburb to the spectacular and hazardous environment of space, and ultimately, to the Moon. Five years in the making, The Last Man on the Moon unveils a wealth of rare archive material, and takes Cernan back to the launch pads of Cape Kennedy, to Arlington National Cemetery and to his Texas ranch, where he finds respite from a past that refuses to let him go.
2014 • Astronomy
The shocking story of Aum Shinrikyo, the doomsday cult that unleashed a deadly nerve gas in Tokyo's subway system in 1995. Founded by disillusioned yoga teacher Shoko Asahara, Aum transformed into a terrorist organization while Japan's police and media turned a blind eye. Featuring rare archival footage and an interview with one of Asahara's former high-ranking disciples.
2023 • People
The inside story of the tech entrepreneurs who created the social media app Twitter. At first the site grew on the back of celebrities who realised it offered them a direct way to communicate with fans. After going global, it seemed to be fulfilling the founders' dream of a digital utopia where all voices would be heard. But as hate speech and misinformation flooded the platform, the founders faced growing problems to control it - and the sale to Elon Musk in 2022 represented the end of their dream.
2025 • Technology
Explore Tulum, the final inhabited city of the Maya empire, where innovative archaeology and cutting-edge technology reveal the mysteries behind the collapse of one of Mesoamerica's greatest civilisations.
2023 • History
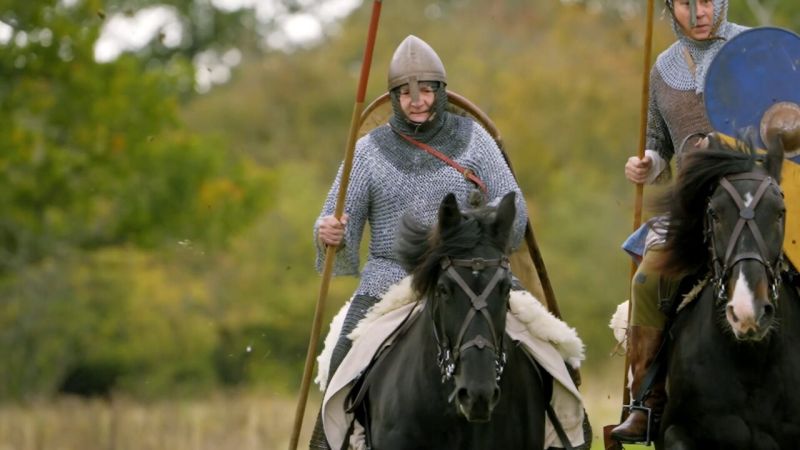
From battlefields and ancient swords to mighty castles and Durham cathedral, the rich, brutal story of William the Conqueror's journey from invader to ruler of England. Alice Roberts discovers who the Normans really were, tests a nearly thousand-year-old sword from William the Conqueror's time and wonders why there are so few women depicted in art from the time. Plus, Danielle George gets a brutal lesson in medieval 11th-century battlefield combat techniques, and Onyeka learns how William's coronation turned into a PR disaster.
S1E4 • Fortress Britain • 2022 • History
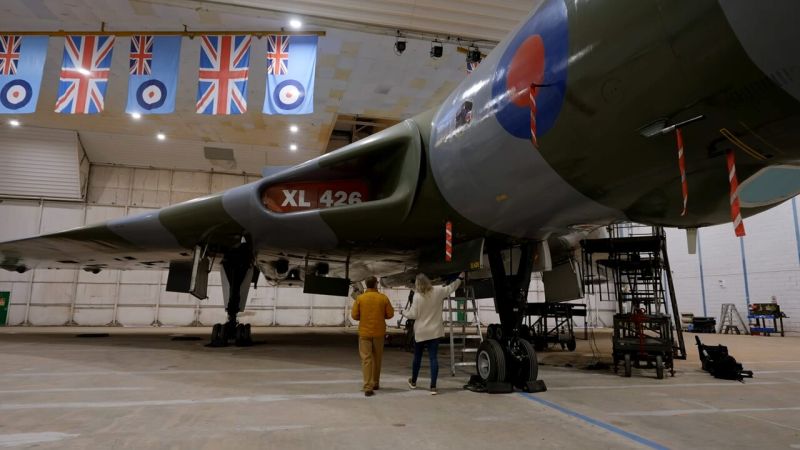
Tales of Cold War Britain, from nuclear threat to upper-class spies, eerie ghost bunkers and our very own Chernobyl. In Cold War military buildup Britain constructed bunkers for the civilian population and created its own nuclear missile defense. Professor Alice Roberts explores the UK's response to the threat of nuclear attack during the early years of the Cold War in the 1950s, when a network of upper-class spies began merrily sharing British military secrets with the Soviet Union. We also visit a nuclear-bomb-proof command center and inspect the legendary Avro Vulcan jet bomber.
S1E3 • Fortress Britain • 2022 • History
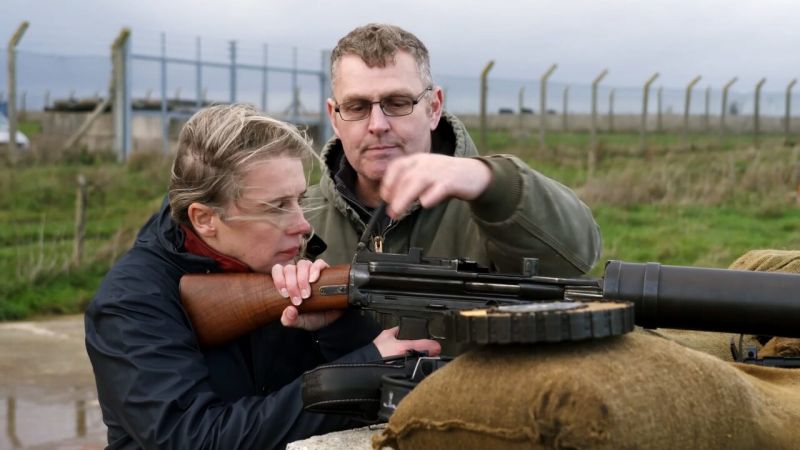
How Britain planned for a Nazi invasion - from tank traps and sticky bombs, to the Home Guard and tragic story of heroism. Alice Roberts looks for visible traces of Britain's rearmament in preparation for a German invasion. How did the Home Guard come about and what was the role of women in the offensive defense? We meet Indian-American Noor Inayat Khan, a special agent who worked with sabotage activities in German-occupied France, and hear her tragic story as one of the war's forgotten heroines. Alice learns about the deployment of the Home Guard, and Danielle travels to the Channel Islands, the only part of the British Isles under German control, to visit the only concentration camp built on British soil in Alderney. She explores life under occupation and visits the underground hospital Festung Guernsey.
S1E2 • Fortress Britain • 2022 • History
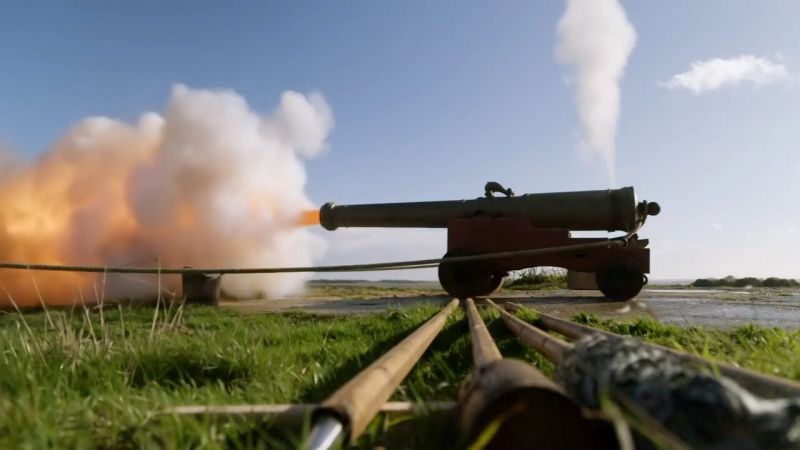
The story of Henry VIII's fear of Catholic Europe, told via his castles, cannons and spies. The first episode examines the surviving traces of Henry VIII's fear of invasion from Catholic Europe through physical reminders, including mighty castles and cannons, that survive to this day. At her headquarter in Walmer Castle, built in 1540 in Kent to defend the town against a French invasion, Alice gets her hands on a vast hoard of Tudor coins and a 500-year-old jousting scorecard, as she learns how Henry's greed and ambition led him to bankrupt the nation and lay the foundations for the modern secret service. Danielle visits Henry's mighty castle at Deal and witnesses the awesome power of the cannons built to defend England, while Onyeka gets within touching distance of the iconic Mary Rose.
S1E1 • Fortress Britain • 2022 • History
In 1966, drought and an exploding population confronted India with the imminent threat of a severe famine that many scientists and intellectuals feared was a harbinger of global catastrophes to come, as the world's population outstripped its ability to produce food. India turned to Norman Borlaug, an unassuming plant breeder from Iowa whose combination of scientific knowledge and raw determination had made him a legend among a small handful of fellow specialists. The Man Who Tried to Feed the World recounts the story of the man who would not only solve India's famine problem, but would go on to lead a "Green Revolution" of worldwide agriculture programs, saving countless lives. He was awarded the 1970 Nobel Peace Prize for his work but spent the rest of his life watching his methods and achievements come under increasing fire.
2020 • People
On the front lines of the hunt for killer viruses, a shocking discovery is made: viruses, once thought to be a menace to humankind, may in fact be the ultimate creators. Since the beginning of time, they have played a critical role in evolution, shaping us and perhaps even creating us. How could that be? How can an entity seemingly programmed for destruction lead to genetic diversity and new species? To many people, viruses are simply agents for disease, but to Dr. Luis Villarreal, Director of the Center for Virus Research at the University of California Irvine, they may possess far greater power than originally thought. He guides us through evidence that viruses gave rise to the first complex cells, played a role in the diversification of life, changed how our young are born, drove evolution, and perhaps gave us emotions. One expert even suggests that an ancient virus could have entered our genes and rewired us for monogamy. National Geographic investigates a provocative new theory that suggests that all life - including humans - is descended from viruses. Taking us through African jungles in search for new strains, this episode of Explorer presents a startling new view of viruses - toward what may be a remarkable evolutionary moment: the rise of a new human species.
2008 • Health
James May charts the journeys of explorers through experiments and messing about in boats. Chapter 1: Christopher Columbus The host profiles famous explorers, beginning with Christopher Columbus. He may be celebrated as a national hero for 'discovering' the USA - but he never set foot there. James starts by travelling to south-west Spain, from where these world-changing voyages began. May takes the helm of his own sailboat to test the cutting-edge sail technology that allowed ships to travel further than ever - and the rudimentary navigation techniques that Columbus had to rely on. Chapter 2: Sir Walter Raleigh James follows Walter Raleigh's rise from rural Devon to London high-society. He meets top barrister Benet Brandreth KC at The Honourable Society of the Middle Temple to learn the techniques of persuasion that allowed Raleigh to talk his way to the top. James also explores the darker and more complex corners of Raleigh's legacy. Chapter 3: Captain Cook Captain James Cook was the last explorer in the age of sail - and one of the busiest, charting one third of the globe. His voyages brought huge advancements in navigation, biology, and geography, and in Britain he is generally thought of as a hero - but in other parts of the world, that's not the story. James May examines how this studious and serious son of a farmer broke through the class ceiling to become the greatest naval captain of his age.
2025 • Travel
Gabriel Gatehouse tries to solve the biggest mystery in tech: who is Satoshi Nakamoto, the creator of Bitcoin? Now a multi trillion-dollar industry, its pseudonymous inventor has not been heard from since 2011. Whoever it is could be one of the richest people on the planet, and yet their identity remains unknown. Whilst on the trail for Bitcoin's inventor, Gabriel uncovers a conspiracy to end democracy and transform the world as we know it.
2025 • Technology
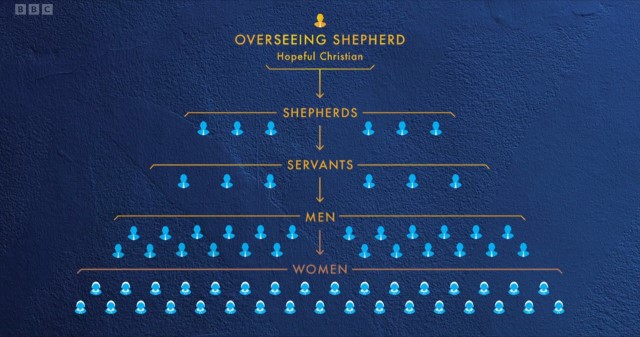
The fight to break free from a New Zealand Christian cult. Gloriavale hides the darkest of secrets - as the promise of heaven on earth descends into seclusion and subordination. Chapter 1: In 1969 an Australian preacher set up a religious community in New Zealand known as Gloriavale. Today it is home to 650 people who live a closeted existence away from the rest of society. This documentary examines the dark secrets at the heart of this Christian sect and the allegations that its followers are indoctrinated to an oppressive existence for life. Chapter 2: Focuses on what life was like for the second and third-generation members of Gloriavale, growing up in a world where every decision is made for them. New Zealand journalist Melanie Reid recounts her experience of going undercover inside the community in the 1990s, and the work she did to try to stop the abuse she discovered. Chapter 3: Charts the impact of the loss of Gloriavale's charismatic leader Hopeful Christian and his successor's struggle to keep the community running. Meanwhile, an underground network helps one member leave, while two former children of Gloriavale expose one of its most shocking secrets.
2025 • People
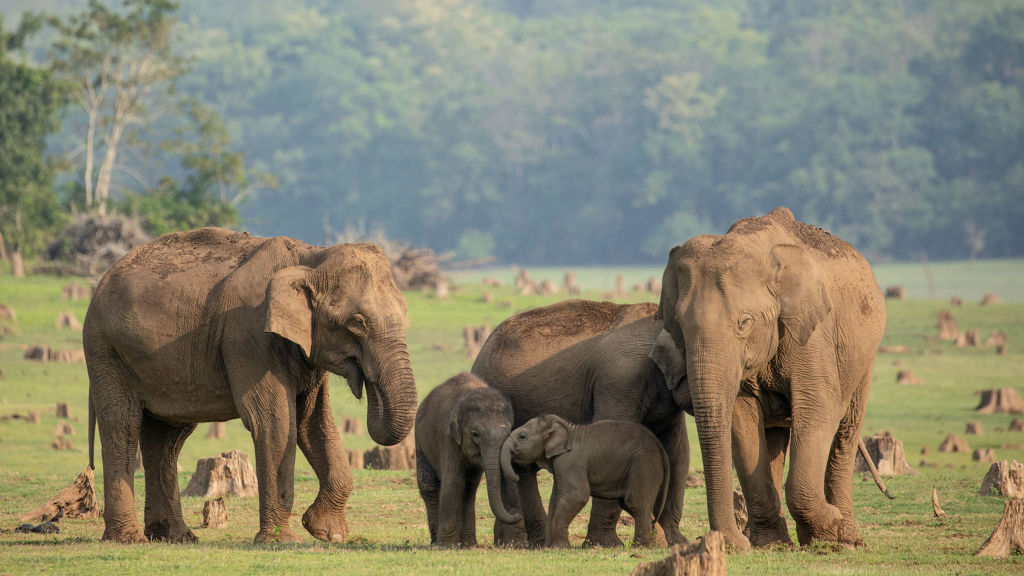
Across Asia, elephants must use their intelligence and understanding of us to adapt to the human world.
S1E4 • Secrets of the Elephants • 2023 • Nature
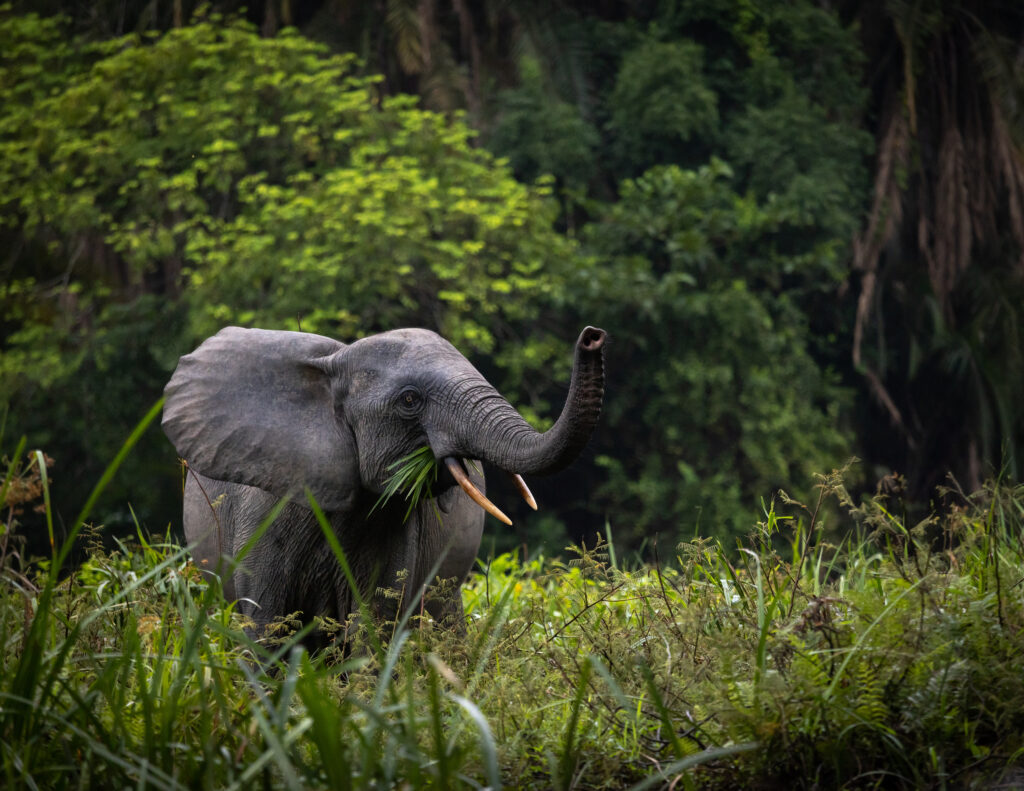
Revealing the secrets of the world's most elusive elephant species and how they have adapted to life in their rainforest home.
S1E3 • Secrets of the Elephants • 2023 • Nature
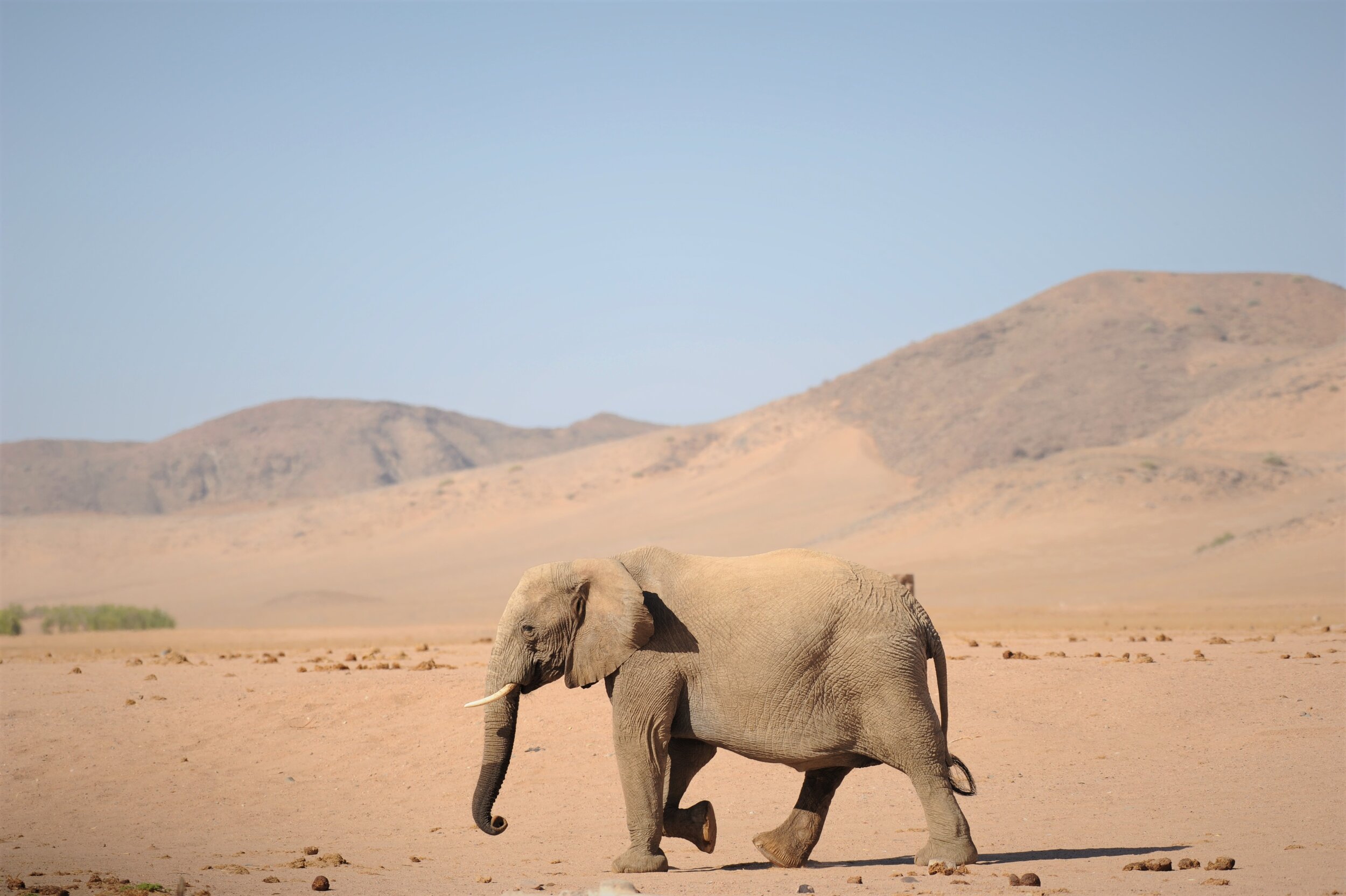
Elephant families face the challenges of life in the deserts of Namibia.
S1E2 • Secrets of the Elephants • 2023 • Nature
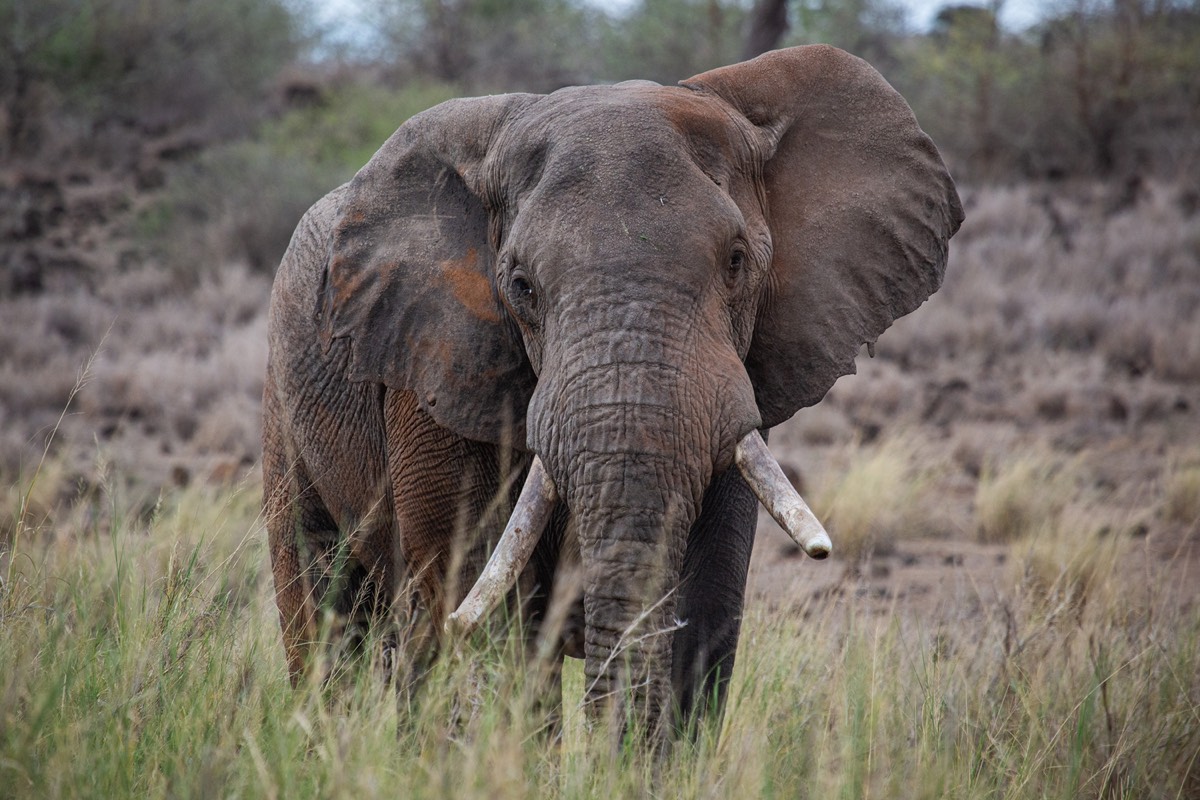
Family relationships are the secret of success for savanna elephants. Emotional bonds and wisdom help them navigate a changing world.
S1E1 • Secrets of the Elephants • 2023 • Nature
The second episode delves into the moral framework that religions are often cited as providing and argues against the indoctrination of children. Dawkins compares religious faith to a virus, being passed from parents to offspring and teachers to pupils. He visits a London Hasidic Jewish school, where students are largely isolated from outside ideas, and Phoenix Academy, a semi-independent city academy following the American Accelerated Christian Learning curriculum. Dawkins interviews the headteacher about the integration of biblical stories into various academic subjects and explores the differences between secular ethics and morality based on religious law. He also discusses concepts from evolutionary biology, such as reciprocal altruism and kin selection, as explanations for morality.
S1E2 • The Root of All Evil • 2006 • People
In the first episode, Dawkins examines the unproven beliefs held as facts by many religions and the extremes to which some followers take them. He argues that faith is not a way of understanding the world but is fundamentally opposed to modern science, which tests hypotheses and builds theories to describe the world. Dawkins visits the United States to interview Pastor Ted Haggard, president of the National Association of Evangelicals, and travels to Jerusalem to interview Yousef al-Khattab, an American-born Jew who settled in Israel before converting to Islam. He uses Bertrand Russell's celestial teapot analogy to respond to charges that scientific understanding does not entitle one to reject religion.
S1E1 • The Root of All Evil • 2006 • People
Levison Wood tracks down some of the most iconic but endangered animals on Earth and gets a better understanding of how they are surviving against worsening odds. Chapter 1: Orangutans Deep in Borneo's forests, Levison meets the last-remaining endangered orangutans, and learns more about their unique lives and their environment, as they face the threat of deforestation and poaching. Chapter 2: Lions In Namibia's extreme environment, Levison tracks down some of the last remaining desert lions and learns about the vital work that's giving them a fighting chance of survival. Chapter 3: Polar Bears Levison travels deep into the vast arctic wilderness of east Greenland to track down some of the most elusive populations of polar bears on the planet. But will he get up close and personal with one?
2023 • Nature
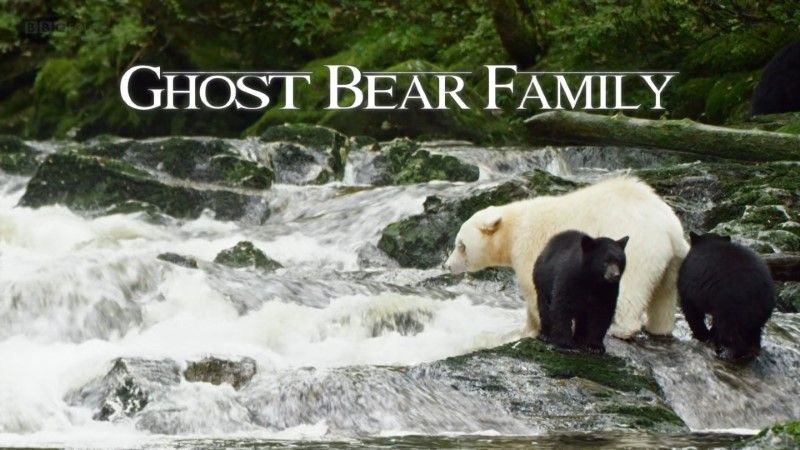
In the vast Canadian wilderness, there lives a very special bear family. Just out of hibernation, two black cubs have a pure white mother. She's not a polar bear or albino - locally she's known as a ghost bear. This far north, winter is never far away, and this unusual family must work hard to find enough food to see them through. They will also need to avoid other large predators, but being so different could bring them unwelcome attention.
2015 • Nature
The forces tearing apart our democracy have never been more frightening or powerful, but who is actually behind them? BAD FAITH reveals how Christian Nationalist leaders have spread fear and anger for decades, distorting political issues into Biblical battles between good and evil. Financed through the secretive Council for National Policy, Christian Nationalists have succeeded in taking over the Republican Party, turning it into a powerful weapon to demolish democracy from within. Discover the origins of this organized grasp for power and the grassroots coalition of secular and interfaith leaders bravely confronting the unholy forces threatening democracy.
2024 • History
By assassinating nearly a third of Europe's workers in some countries, World War 1 reduced the militant mass to silence. But it was above all the repressive measures of the major democracies that, from deportations to executions, dealt a blow to the anarchist movement. In this fertile inter-war period, where capitalism gave birth to its two foul beasts, Stalinism and fascism, more than ever before, anarchism continued to be the only force of resistance for the people, in the face of the totalitarian hydra that was increasingly generalising theft and industrialising death. From Boston to Barcelona, from Tokyo to Paris, anarchism was to lead a struggle on all fronts. It was eventually in Spain, during the course of a war resembling a revolution that the movement finally came within reach of utopia.
S1E3 • No Gods, No Masters: A History of Anarchism • 2016 • History
At the start of the 20th century, everything seemed to be plain sailing in the best possible of libertarian worlds, because anarchism had rid itself of its former demons. And thanks to the major waves of migration that carried the movement to the remotest areas of the world, it was able to rally a major part of the peasantry around to its cause. But to ensure their ideal triumphed, before the imminence of a world conflict, libertarians could no longer afford merely to indulge in wishful thinking and think up generous practices. They must take up arms and go on the offensive once again. And so, from the two shores of Mexico to the vast steppes of the Ukraine, in an era full of sound and fury, Nestor Makhno and the Flores Magon brothers found themselves at the forefront of the first major revolutions of the 20th century as they tried, once and for all, to change the world.
S1E2 • No Gods, No Masters: A History of Anarchism • 2016 • History
Born in France, around the Commune de Paris, and in the wake of the French Revolution, anarchism rapidly disseminated its theories throughout the world. When the brand new International Workers' Association was created, anarchism even became predominant within the workers' movement. Yet early on, anarchism instilled fear in people, not only because all over the world it waged the war for an 8-hour working day, founded schools with no God and no master, and promoted free love, but also, and above all, because from time to time it was quick to use violence and to destroy authority in a highly concrete way. From Ravachol to Bonnot, from the assassination of Empress Sisi of Austria to the Battle of Stepney, from bombs to raids, anarchism has become the bete noire of heads of states and royalty who, in an attempt to protect themselves from it, created anti-terrorist laws that are still in force today.
S1E1 • No Gods, No Masters: A History of Anarchism • 2016 • History
While most know chicken as a dinner-plate staple, few pause to consider this bird’s many virtues. In this fascinating and gently comic documentary, director Mark Lewis delves into the under-recognized complexities of this seemingly simple animal. Through interviews with those who have formed unique bonds with chickens and narrative vignettes depicting the birds at their magical best, Lewis allows us to rethink our relationship to a creature we have previously taken for granted, while at the same time providing a lens through which we can view ourselves anew.
2000 • Nature
In the summer of 1950 fear gripped the residents of Wytheville, Virginia. Movie theaters shut down, baseball games were cancelled and panicky parents kept their children indoors — anything to keep them safe from an invisible invader. Outsiders sped through town with their windows rolled up and bandanas covering their faces. The ones who couldn't escape the perpetrator were left paralyzed, and some died in the wake of the devastating and contagious virus. Polio had struck in Wytheville. The town was in the midst of a full-blown epidemic. That year alone, more than 33,000 Americans fell victim — half of them under the age of ten.
2009 • Health
Cullen Hoback investigates the origins of Bitcoin and its anonymous creator Satoshi Nakamoto, exploring the potential of this cryptocurrency on the global financial system and who could hold immense power if it became mainstream.
2024 • Economics
Can technology help eradicate infectious diseases? Bill meets with Dr. Anthony Fauci and other public health experts to examine the latest breakthroughs.
S1E5 • What's Next: The Future with Bill Gates • 2024 • Technology
The income gap is a growing concern with far-reaching implications. Bill explores ways to address inequality with Sens. Bernie Sanders and Mitt Romney.
S1E4 • What's Next: The Future with Bill Gates • 2024 • Technology
Gates tackles the efficacy of fighting climate change, weighing the cost-benefit analysis that future generations will inevitably have to confront.
S1E3 • What's Next: The Future with Bill Gates • 2024 • Technology
Preserving truth in an era of misinformation is challenging. Bill traces the life cycle and impact of conspiracy theories, with insights from Lady Gaga.
S1E3 • What's Next: The Future with Bill Gates • 2024 • Technology
Love or loathe him, Microsoft founder Bill Gates presents an easily digested documentary series on the threats and opportunities facing humanity now and in the future.
S1E1 • What's Next: The Future with Bill Gates • 2024 • Technology